Asbestos
- Asbestos Home
- Did You Know
- Enforcement
- Professionals
- Find a Contractor or Consultant
- Look up Individual Asbestos Licenses
- Asbestos Licensing
- Floor Tile Removal
- Homeowner Information
- Laboratories
- Products Containing Asbestos
- Schools
- Work Practices
- File a Complaint Related to Asbestos
- Minnesota Statutes and Rules
- Resources
- Contact us
Related Topics
Environmental Health Division
Health Effects
Why is asbestos dangerous?
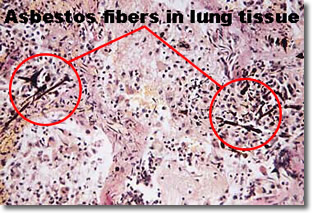
Asbestos is dangerous because it has the ability to break down into microscopically thin fibers. These fibers are so small they can remain airborne for days after they were initially disturbed. While airborne, individuals can breathe these fibers in. Since the fibers are so small, they can travel deep into a person’s lungs, where they may eventually lodge in the lung tissue. Once lodged in the lung tissue, these fibers can cause several serious diseases, including lung cancer, asbestosis (a scarring of the lung tissue) and mesothelioma (cancer of the lining of the lung cavity).
 |  |  |
When is asbestos dangerous?
All types of asbestos fibers are dangerous if you breathe them. Some people say that some kinds of asbestos fibers are less dangerous. Many people, including doctors and scientists, disagree. Until proven safe, treat all asbestos as dangerous.
You cannot tell when asbestos is in the air or is hurting your lungs. Asbestos will not make you cough or sneeze. It will not make your skin or throat itch. Asbestos fibers get into the air when asbestos materials are damaged, disturbed or removed unsafely. When asbestos is crushed, it does not make ordinary dust. Asbestos breaks into tiny fibers that are too small to see, feel or taste.
Asbestos fibers can be measured when they are in the air. They are measured in units called fibers per cubic centimeter of air (f/cc). A cubic centimeter is about the size of a sugar cube. The air is checked for asbestos fibers by taking samples of the air using air sampling methods. The Minnesota Department of Health has established a "clean air" level of 0.01 f/cc.
When asbestos is released into the air, it enters the surrounding environment. You can be exposed to asbestos if you enter these environments. If exposed to asbestos, many factors contribute to whether harmful health effects will occur. These factors include:
- dose (how much);
- duration (how long);
- the route or pathway by which you are exposed (breathing, eating, or drinking); and
- other chemicals to which you are exposed.
Individual characteristics may also have an effect, such as:
- age;
- gender;
- nutritional status;
- family traits;
- lifestyle; and
- your general state of health.
How do we know that asbestos can make you sick?
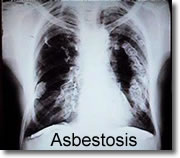
Laboratory studies and studies of asbestos workers show us that asbestos can make you sick. If you breathe asbestos fibers, you may increase the risk of several serious diseases, including asbestosis, mesothelioma and lung cancer.
Asbestos exposure may increase your risk for cancers of the digestive system, including colon cancer.
How much asbestos is dangerous?
No amount of asbestos is considered safe. Products that contain greater than 1 percent of asbestos minerals are considered to be asbestos-containing.
The more asbestos you are exposed to, the more likely you are to get an asbestos disease. Asbestosis and lung cancer are dose-related diseases. Dose-related means the more asbestos you breathe, the more likely you are to get sick.
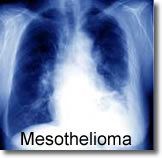
The one asbestos disease that is different is mesothelioma. Very small amounts of asbestos can give you mesothelioma. Asbestos workers' families have gotten mesothelioma from the dust the workers brought home on their clothes.
How long does it take to get sick from asbestos?
All of the asbestos diseases have a latency period. The latency period is the gap between the time you breathe asbestos and the time you start to feel sick. The latency period for asbestos diseases is between 10 to 40 years. You will not feel sick during the latency period. If you get an asbestos disease, you will begin to feel sick after the latency period.
Not everyone exposed to asbestos gets an asbestos disease. However, anyone exposed to asbestos has a higher risk of getting an asbestos disease. All of the asbestos diseases are difficult to treat. Most are impossible to cure. Stopping asbestos fibers from ever entering your lungs is important. The only cure for most asbestos diseases is to prevent them.
Is there any way of knowing if I have been exposed to asbestos?
The most common test used to learn if you have been exposed to asbestos is a chest x-ray. The x-ray cannot detect the asbestos fibers themselves, but can detect early signs of lung disease caused by asbestos. Other tests, such as lung scanning and computer-aided tomography (CAT scan), are also useful in detecting changes in the lungs.
How do I find out more information?
For more information about asbestos, contact the Asbestos Program at MDH through the internet or by telephone at (651) 201-4620.
Go to > top