Contact Info
Infectious Disease Epidemiology, Prevention and Control Division
651-201-5414
Pregnancy and Vaccination
Appropriate vaccination can prevent serious complications from infectious disease for pregnant persons, the fetus, and newborns.
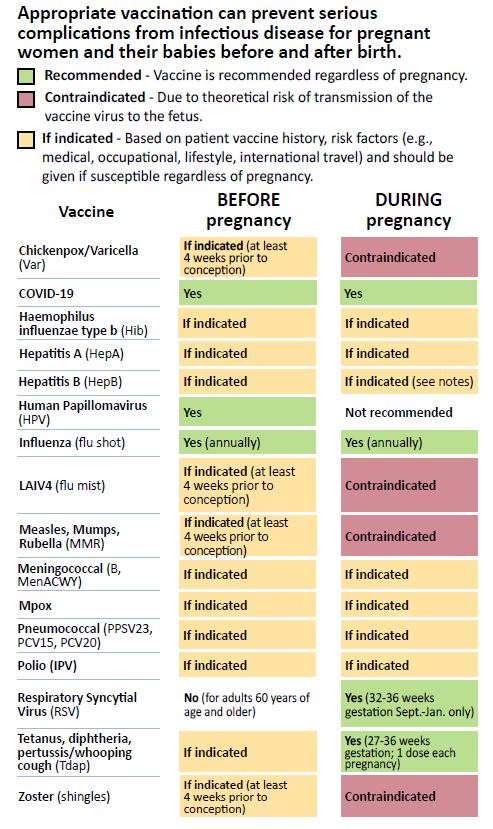 | Pregnancy and Vaccination Pocket Guide (PDF) A guide for health care providers that outlines vaccination decisions prior to pregnancy, during pregnancy, after pregnancy and in the baby's first year. Printed guides are available for order at Order Printed Immunization Materials. |
- CDC: Pregnancy and Vaccination
CDC's toolkit for prenatal care providers for increasing the use of maternal vaccines by ob-gyns, nurse-midwives, and other health care professionals.
Tdap/Td
- Give Tdap between 27- and 36-weeks' gestation during each pregnancy, preferably earlier in that timeframe.
- Tdap can be given regardless of the interval since last Td or Tdap.
- Give Tdap instead of Td for wound management during pregnancy.
- Pregnant women who never received a primary Td series should receive three doses. Give Td/Tdap at intervals of 0, 1, and 6 months. One of the three doses should be Tdap, preferably given between 27-36 weeks.
Vaccine-related prenatal serologic screening
- Test for rubella immunity: if susceptible, vaccinate postpartum. If a woman of childbearing age has documentation of three MMR vaccinations, no further testing or MMR vaccination is recommended.
- Test for hepatitis B infection: vaccinate if susceptible and at risk. Send results to birthing hospital; if HBsAg-positive, report results to the Minnesota Department of Health.
Vaccinating household contacts of pregnant women
- Make sure household contacts of pregnant women are up to date on:
- Pertussis-containing vaccines (Tdap or DTaP depending on age).
- Influenza vaccine.
- Hepatitis B if pregnant woman is HBsAg-positive.
- No vaccine - except smallpox - is contraindicated for household contacts or the children of a pregnant woman.
Vaccinating breastfeeding women
- Neither inactivated nor live-virus vaccines given to a breastfeeding woman affect the safety of breastfeeding for mothers or infants with a couple of exceptions:
- Breastfeeding is a precaution to yellow fever vaccination.
- Breastfeeding is a contraindication for smallpox vaccination.
Protecting newborns
- Vaccinating pregnant women allows antibodies to be passed to the fetus. The antibodies protect the newborn in the first few weeks of life until they can start receiving their own vaccinations.
- Stress the importance of childhood immunization, starting with the hepatitis B vaccine in the first 24 hours of life.
Last Updated: 10/23/2024