Radon
- Radon in Homes
- Radon Testing
- Radon in Real Estate
- Find a Radon Measurement Professional
- Find a Radon Mitigation Professional
- Radon Mitigation Systems
- Financial Assistance
- Radon Resistant New Construction
- Licensing for Radon Professionals
- Laws, Rules and Standards
- Radon Poster Contest
Related Topics
Environmental Health Division
Radon Testing
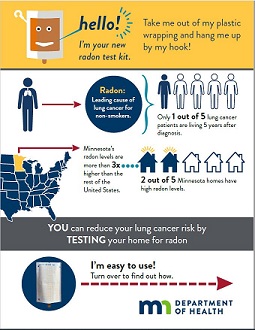
MDH recommends that all Minnesota homeowners test their homes for radon. A radon test is the only way to find out how much radon is in your home. You can test your home yourself or hire a licensed professional. Most radon tests can be performed on your own, after reading the instructions. Hiring a radon measurement professional is recommended when an unbiased, third party is needed, such as in a real estate transaction. The result(s) from a properly performed radon test will help you decide if you need to reduce your home's radon level.

Download a printable version of the brochure on radon testing:
radon: A brief guide on how to keep you safe from radon (PDF)
- Hmong - Cov pa radon: lus qhia luv txog txoj hau kev los ceev koj kom muaj kev nyab xeeb ntawm cov pa radon (PDF)
- Karen - radon: A brief guide on how to keep you safe from radon (PDF)
- Somali - radon: Tusmo kooban oo ku saabsan sida gurigaaga looga ilaaliyo radon (PDF)
- Spanish - El radón: Una breve guía sobre cómo mantenerse seguro en relación con el radón (PDF)
Download a printable version of the information sheet on directions how to use the Air Chek test kit:
Radon: How to test using the Air Chek test kit (PDF)
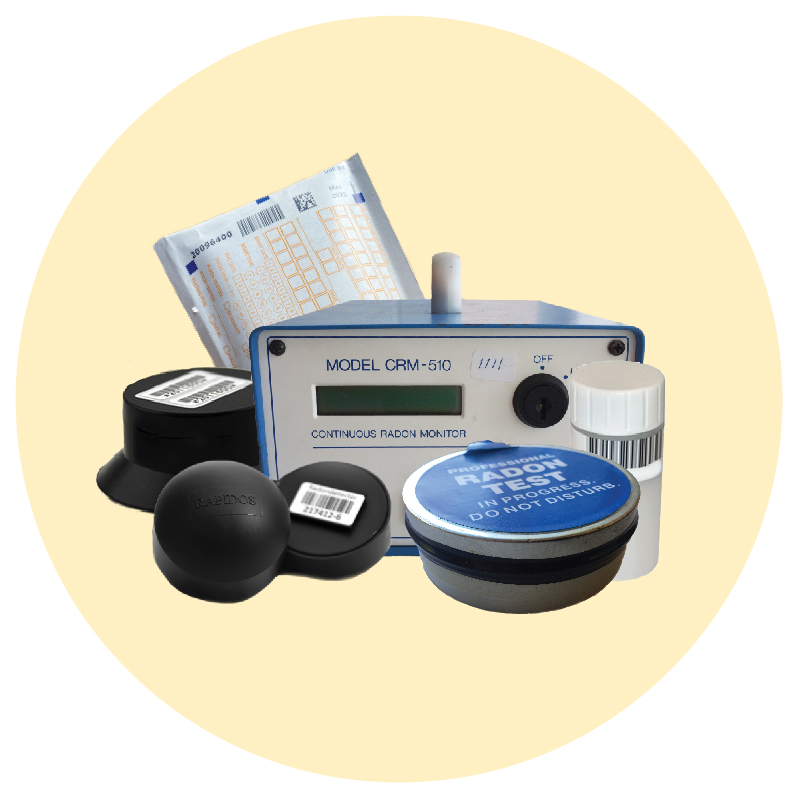
Types of radon test kits
There are two basic types of radon tests:
Short term - A short-term test typically measures radon levels for 2-7 days and is a quick way to screen a home for radon. When you test for radon you should start with a short-term test.
Long term - A long-term test measures radon levels for a minimum of 90 days. They are the best way to estimate the annual average of radon in the home. Long-term testing should include both heating and non-heating seasons.
(Click on image to enlarge)
How often should I test for radon?
- All Minnesota homes should be tested for radon and then retested every 2-5 years (save your test results).
- Test before and after you make changes to the home, including finishing a basement, adding an addition, making energy efficiency improvements (replacing windows or adding insulation), or installing a vent hood in the kitchen. This also includes if you add or modify your home’s central air conditioning or heating system. Retest after adding a radon mitigation system to make sure it is working properly.
Where can I get a radon test kit?
Radon test kits are inexpensive and are available at many local health departments, hardware stores, laboratories, and other vendors. Some test kits may also require an analysis fee paid when mailing the kit to the lab. •
- Air Chek, Inc. - A manufacturer of short-term radon test kits. Minnesota residents receive a discount. Order online: Air Chek
- Local Agencies - Many local agencies distribute radon information and some distribute radon test kits to their residents, see the list of Local Radon Contacts.
- Online Laboratories and Vendors - Search for ‘short term radon test kit’ or ‘long term radon test kit’.
Radon testing guidelines
- Instructions - Read the instructions that come with the radon test kit and fill out the information. Check the expiration date on the kit.
- Time of year - Short-term tests can be completed any time of year, but the heating season is the best time to test. Long-term tests should include some of the heating and non-heating seasons.
- Weather - Weather can affect the radon levels in the home. If there is severe or unusually windy weather, wait to perform a short-term test.
- Test location - Test the lowest level of the home that is regularly used. For example, if you spend more than 10 hours a week in the basement, we recommend testing the basement. For real estate transactions, test the lowest level of the home such as the basement.
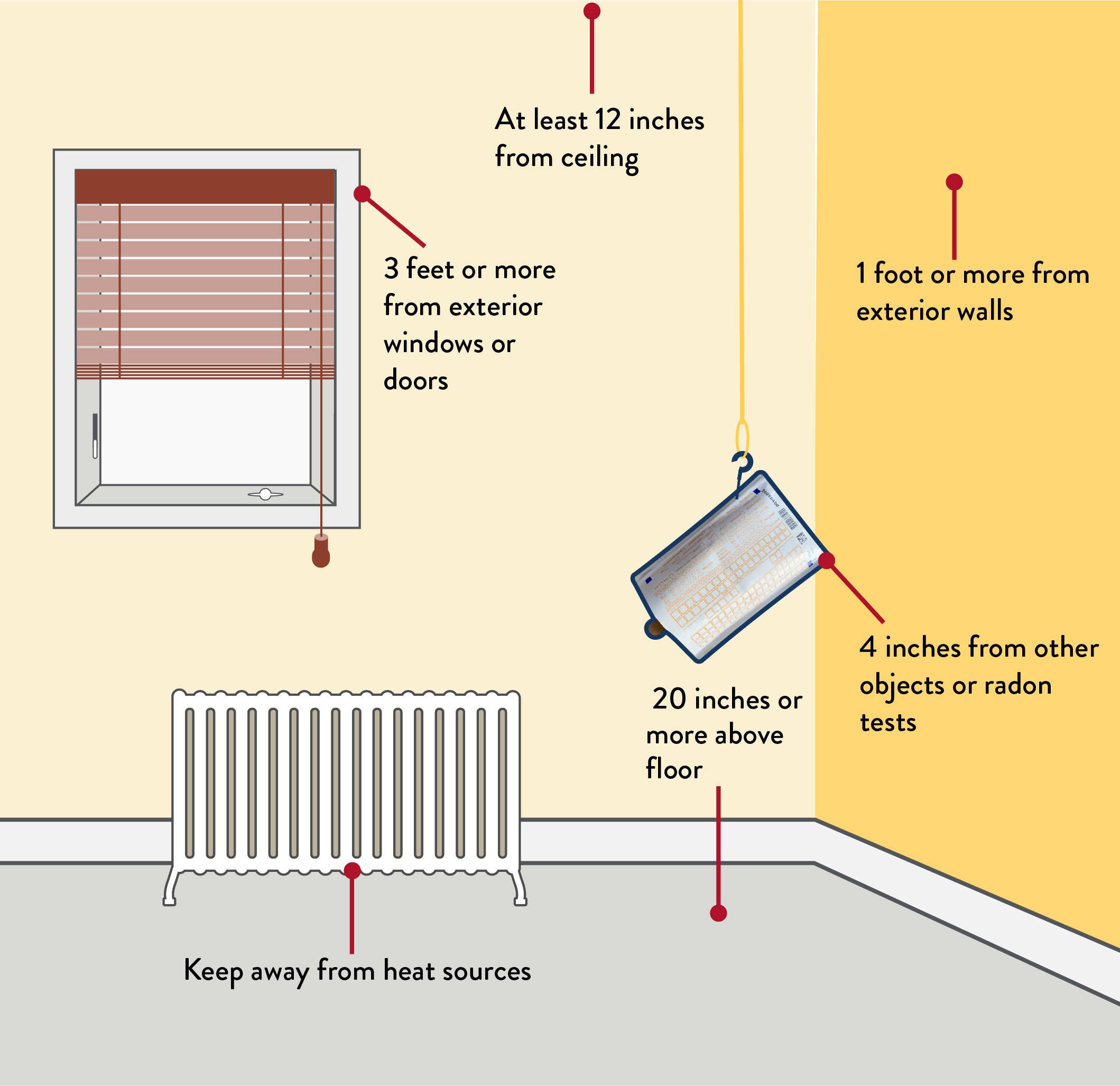
- Test placement - Place the test kit at least 20 inches above the floor, preferably at your “breathing level”. . Keep the kit 1 foot from exterior walls, 3 feet from exterior windows, and away from drafts. Keep away from high humidity areas like kitchens, baths, and laundry rooms. Keep away from heat areas like fireplaces and furnaces. (See Test kit placement image below)
- Home Conditions - Any test lasting less than 3 months requires closed-house conditions. This means keeping all windows and exterior doors closed, except for normal entry and exit. Run the heating and air conditioning system as you normally would.
Test kit placement
(Click on image above to enlarge)
How to perform a short term radon test
Radon test results
You should complete two tests before deciding to install a radon mitigation system, except when a professional uses a continuous radon monitor as part of a real estate transaction.
When testing for radon start with a short-term test. The results from your first test will determine what your next steps will be. If the result is 0 to 1.9 pCi/L, retest every 2 to 5 years. If the test result is 2 to 7.9 pCi/L, perform a long-term follow-up test. If the test is 8 pCi/L or greater, perform a short-term follow-up test. (Click on image below to enlarge)
(Click on image above to enlarge)
The follow-up test will determine if you need to mitigate. Use the average of the two short-term test results or the result of the one long-term test. If the result is 4 pCi/L or greater, we recommend mitigating. If the result is 2 to 3.9 pCi/L consider installing a radon mitigation system. If the result is below 2 pCi/L retest every 2 to 5 years.

(If the first test was 8 pCi/L or greater, consider performing a long-term test.)
(Click on image above to enlarge)
Go to > top